
Introduction
HTML stands for Hyper Text Markup Language.
HTML is the standard markup language for creating Web pages.
HTML describes the structure of a Web page.
HTML consists of a series of elements.
HTML elements tell the browser how to display the content.
HTML elements label pieces of content such as "this is a heading", "this is a paragraph", "this is a link", etc.
Basic structure of html
An HTML document's basic structure consists of5 elements:
<!DOCTYPE>
<html>
<head>
<title>
<body>
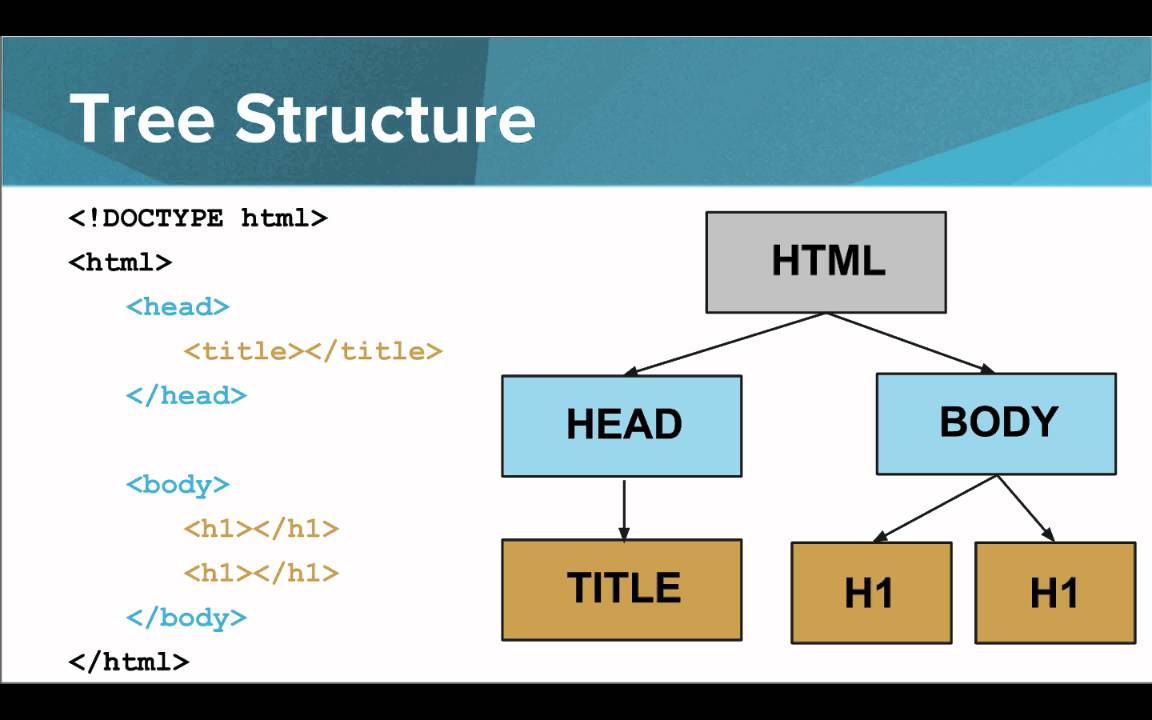
HTML document is divided into two parts :
An HTML Document is mainly divided into two parts:
1.HEAD
This contains the information about the HTML document.
This contains the information about the HTML document. For Example, the Title of the page, version of HTML, Meta Data, etc.
Syntax of the <head> Tag
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
...
</head>
</html>
2.BODY
This contains everything you want to display on the Web Page.
The <body> tag in HTML specifies the main content of an HTML document that appears on the browser. It can contain headings, text, paragraphs, photos, tables, links, videos, etc.
Syntax of the <body> Tag
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>Body Tag</title> </head> <body> <h1>...</h1> <p>...</p> </body> </html>
HTML Headings
HTML Heading tag helps us to give headings to the content of a webpage. These tags are mainly written inside the body tag. HTML provides six heading tags from <h1> to <h6>. Every tag displays the heading in a different font size.
Syntax
<h1></h1>
<h2></h2>
<h3></h3>
<h4></h4>
<h5></h5>
<h6></h6>
This example illustrates the Basic HTML structure.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>My web page</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello, world!</h1>
<p>This is my first web page.</p>
<p>It contains a
<strong>main heading</strong> and <em> paragraph </em>.
</p>
</body>
</html>
Browser Output

In this example, the html element is the root element of the hierarchy and contains two child elements: head and body. The head element, in turn, contains a child element called the title, and the body element contains child elements: h1 and p.
Let's see the meaning of the various elements used in the above example.
<html>: the root element of the DOM, and it contains all of the other elements in the code<head>: contains metadata about the web page, such as the title and any linked CSS or JavaScript files<title>: contains the title of the web page, which will be displayed in the web browser's title bar or tab<body>: contains the main content of the web page, which will be displayed in the web browser's window<p>: contains the paragraphs of text on the web page<strong>,<em>: child elements of the<p>elements, they are used to mark text as important and emphasized respectively
Advantages of HTML
HTML is used to build websites.
It is supported by all browsers.
It can be integrated with other languages like CSS, JavaScript, etc.
Disadvantages of HTML
HTML can only create static web pages. For dynamic web pages, other languages have to be used.
A large amount of code has to be written to create a simple web page.
The security feature is not good.